A proper Amazon pricing strategy is crucial for maximizing sales and profitability. With a vast array of competitors and an informed customer base, getting your pricing strategy right can be the difference between success and failure. This article delves into various aspects of pricing, offering a comprehensive guide to setting competitive yet profitable prices.
1. Market Research and Price Benchmarking
Before setting a price for your product, it’s essential to understand the market landscape. Start by identifying your direct competitors and analyzing their pricing strategies. Pay attention to:
- Common Price Points: Determine the standard prices for similar products. Note any patterns, such as products clustered around specific price ranges.
- Pricing Tiers: Look for distinctions between budget, mid-range, and premium products. Identify what features or benefits are offered at each tier.
Tools like Keepa, Acosbot, or CamelCamelCamel can be invaluable, providing historical price data and trends. This information helps you understand how prices fluctuate over time and can inform your pricing decisions.
2. Value-Based Pricing
Value-based pricing involves setting a price based on the perceived value of your product to the customer. This strategy is particularly effective if your product offers unique features, superior quality, or other distinguishing factors. To implement value-based pricing:
- Highlight Unique Features: Use your product listing to emphasize unique features or benefits that set your product apart.
- Communicate Quality: Use high-quality images, detailed descriptions, and A+ Content to convey the superior quality or craftsmanship of your product.
- Targeted Messaging: Tailor your messaging to address the specific needs and desires of your target audience. For example, eco-friendly products can be marketed to environmentally conscious consumers willing to pay a premium.
3. Cost-Plus Pricing
Cost-plus pricing ensures that all your costs are covered while allowing for a profit margin. To calculate your price:
Calculate Total Costs:
Include manufacturing, shipping, Amazon fees (such as referral and FBA fees), and any additional costs like marketing expenses.
Add Profit Margin:
To determine a reasonable profit margin, you need to understand both the markup and the final margin percentage. The profit margin is essentially the percentage of the final selling price that is profit after all costs have been covered. Here’s how to calculate it:
Determine Desired Profit Margin Percentage:
Decide on the percentage of the final price that you want as profit. For instance, if you aim for a 20% profit margin, you are seeking to make 20% of the selling price as profit.
Calculate Selling Price: Use the formula:
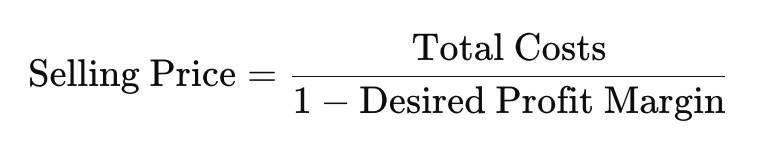
For example, if your total costs are $20 and you want a 20% profit margin, you would calculate:
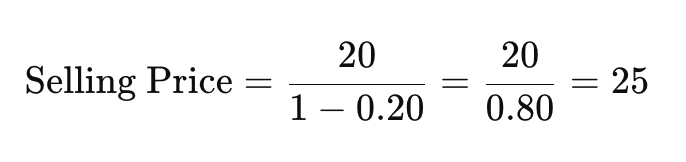
So, your selling price should be $25 to achieve a 20% profit margin.
Confirm Profit Margin: To confirm, subtract your total costs from the selling price and then divide by the selling price to get the profit margin:
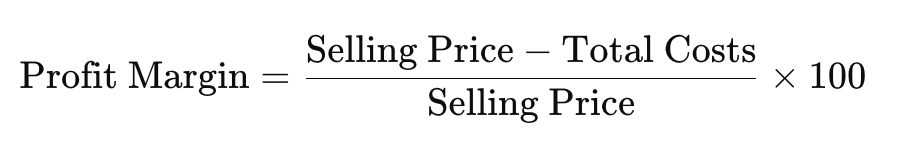
Using the example above:
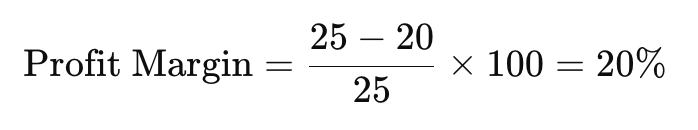
This method ensures that you not only cover all costs but also achieve the desired level of profitability. It’s crucial to choose a profit margin that balances competitiveness with profitability, taking into account market conditions and your business goals.
4. Psychological Pricing
Psychological pricing is a strategic approach that leverages consumer psychology to make products more appealing and encourage purchases. This tactic involves setting prices in a way that influences perception, often making products seem more affordable or valuable than they actually are. Here are some common psychological pricing strategies:
Charm Pricing
Charm pricing, also known as “odd pricing,” is a technique where prices are set just below a round number. For example, pricing a product at $19.99 instead of $20.00. The rationale behind this strategy is that customers tend to focus on the first number they see. In this case, $19.99 is perceived as being in the “teen” range, while $20.00 is seen as being in the “twenties,” despite the minimal actual difference. This small adjustment can significantly impact a customer’s perception of the price, making it seem lower and more attractive.
Left-Digit Effect
The left-digit effect is closely related to charm pricing. It refers to the phenomenon where the leftmost digit disproportionately influences the perceived magnitude of a number. For instance, consumers perceive a price of $4.99 as closer to $4 than $5, even though the difference is only one cent. This effect can make a significant difference in consumer behavior, especially for products priced near a psychological threshold.
Price Anchoring
Price anchoring involves setting a reference point (the anchor) that customers can use to compare the price of a product. This can be done by displaying an original price alongside a discounted price, making the discount appear more substantial. For example, showing that an item was originally $50 and is now $30 can make the $30 price seem like a bargain, even if the original price was artificially inflated.
Decoy Pricing
Decoy pricing introduces an option that is not intended to be sold but instead makes other choices more attractive. For example, offering three product versions at $20, $50, and $55, where the $50 version is similar to the $55 version but lacks a few key features. The $55 version appears as a better deal because it offers more value for only a small additional cost, steering customers towards the higher-priced option.
Bundling and Perceived Value
Bundling involves offering multiple products together at a lower price than if they were purchased separately. This strategy enhances perceived value, as customers feel they are getting more for their money. For instance, offering a set of kitchen utensils at $49.99, which separately would cost $70, emphasizes the deal’s attractiveness and can prompt quicker purchasing decisions.
Prestige Pricing
Prestige pricing sets prices higher than average to create an impression of quality and exclusivity. This strategy works particularly well for luxury items or premium brands. For example, a watch priced at $299 instead of $199 might convey higher quality, craftsmanship, and status. Consumers often associate higher prices with better quality, so setting a high price can enhance the product’s perceived value.
Even and Odd Pricing
In some markets, prices ending in odd numbers (e.g., $9.99) are perceived as discounts or good deals, while prices ending in even numbers (e.g., $100) are associated with higher quality or luxury. Choosing the appropriate strategy depends on the brand image you want to convey and the consumer segment you are targeting.
Scarcity and Urgency
Creating a sense of scarcity or urgency can also play into psychological pricing. Limited-time offers, countdown timers, and statements like “Only 3 left in stock” can encourage consumers to act quickly, fearing they might miss out on a good deal. This strategy can effectively increase the perceived value of a product and prompt immediate purchases.
5. Dynamic Pricing
Dynamic pricing involves adjusting prices based on real-time market conditions, demand, and competitor actions. This approach helps you stay competitive and can be crucial during peak shopping periods or in response to market shifts. Utilize repricing tools that automatically adjust prices within a predetermined range. This strategy allows for agility and can optimize both sales volume and profitability.
6. Promotional Pricing
Promotions and discounts can attract new customers and boost sales, but they should be used strategically:
- Limited-Time Offers: Use promotions like Lightning Deals or Daily Deals to create urgency.
- Coupons: Offer digital coupons that customers can apply at checkout, which can be an effective way to increase conversion rates.
- Bundling: Combine products and offer them at a discounted price, encouraging customers to purchase more.
While promotional pricing can increase sales volume, it’s essential to avoid overuse, which can devalue your product.
7. Monitoring and Adjusting Prices
Regularly review your pricing strategy to ensure it remains competitive and profitable. Key metrics to monitor include:
- Sales Velocity: How quickly your product is selling.
- Conversion Rates: The percentage of visitors who purchase your product.
- Profit Margins: The difference between your selling price and total costs.
If you notice a drop in sales, consider whether your pricing needs adjustment. Conversely, if sales are strong and steady, you might explore the potential for price increases.
8. Understanding Amazon Fees
Amazon charges various fees, including referral fees, FBA fees, and potential costs for premium services like Prime eligibility. These fees can significantly impact your profit margins, so it’s crucial to account for them when setting your prices. Misjudging these costs can lead to underpricing and reduced profitability.
9. Price Matching and the Buy Box
Winning the Buy Box is a critical aspect of selling on Amazon, as it directly influences your product’s visibility and sales potential. Price is a key factor in Buy Box eligibility, alongside seller metrics and availability. In highly competitive categories, consider price matching to maintain a competitive edge and increase your chances of winning the Buy Box.
10. Integrating Amazon PPC with Pricing Strategy
Amazon PPC (Pay-Per-Click) advertising is a crucial component of your overall pricing strategy. PPC campaigns can drive targeted traffic to your listings, but they also incur costs that must be factored into your pricing. A successful PPC strategy involves balancing your ad spend with product pricing to ensure profitability. By analyzing data from PPC campaigns, such as conversion rates and ACOS (Advertising Cost of Sales), you can refine your pricing to optimize both ad performance and overall sales. Additionally, PPC data can provide insights into which keywords and product features resonate most with customers, allowing you to adjust your pricing and product positioning accordingly.
Conclusion
Effective pricing is a dynamic and multifaceted aspect of selling private label products on Amazon. By employing a blend of market research, value-based considerations, psychological tactics, and dynamic adjustments, you can find a pricing sweet spot that maximizes both sales and profitability. Regular monitoring and adaptation to market changes, along with the integration of Amazon PPC insights, will help maintain your competitive edge, ensuring your products remain attractive and accessible to your target customers.



